Back

Diabetes in Practice
(P304) Changes in Glycemic Management after Initiating CGM and DSMES in Men with Type 2 Diabetes
Friday, August 12, 2022
12:00 PM – 1:00 PM ET

Has Audio

Kim Stote, PHD, MPH, RDN
Research Associate
Stratton VA Medical Center
Albany, New York, United States
Primary Presenter(s)
Key Takeaways of Your Research: The research findings suggest that in men with type 2 diabetes, initiation of continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) under supervision of a diabetes self-management education and support specialist, may experience improved glycemic management with reduction of HbA1c and hypoglycemia along with other improvements in CGM metrics such as in time in range.
Background/Purpose: Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) use has grown rapidly. In clinical trials, CGM and diabetes self-management education and support (DSMES) show clinical benefits such as reduction of HbA1c, reduction of hypoglycemia and the increase of the amount of time glucose values are in target range. However, less is known about the efficacy of CGM use in real world clinical settings. Research Hypothesis and/or Research Questions and Specific
Aims: CGM along with DSMES improves HbA1c and glucose management metrics for clinical care in persons with type 2 diabetes. Methods/Methodology: This retrospective observational study examined twelve months of data collected from existing medical records at the Stratton VA Medical Center, Albany, NY. HbA1c and CGM metrics were analyzed in patients with type 2 diabetes who started to use CGM beginning in January 2019 or later. This study was approved by the IRB of the Stratton VA Medical Center.
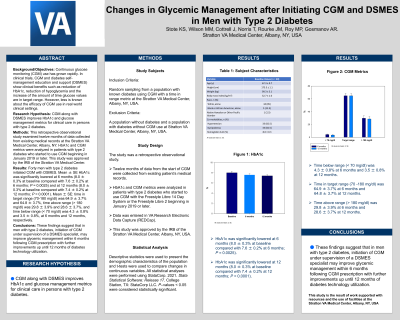
Results: Forty men with type 2 diabetes initiated CGM with DSMES. Mean ± SE HbA1c was significantly lowered at 6 months (8.0 ± 0.3% at baseline compared with 7.6 ± 0.2% at 6 months; P = 0.0025) and at 12 months (8.0 ± 0.3% at baseline compared with 7.4 ± 0.2% at 12 months; P = 0.0001). Mean ± SE: time in target range (70-180 mg/dl) was 64.9 ± 3.7% and 64.8 ± 3.7%, time above range (> 180 mg/dl) was 29.8 ± 3.9% and 28.6 ± 3.7%, and time below range ( < 70 mg/dl) was 4.3 ± 0.8% and 3.5 ± 0.8%, at 6 months and 12 months, respectively. Conclusions (Impact on Diabetes Care and Education): These findings suggest that in men with type 2 diabetes, initiation of CGM under supervision of a DSMES specialist may improve glycemic management within 6 months following CGM prescription with further improvements up until 12 months of diabetes technology utilization. Source of Funding for this Research: The study is the result of work supported with resources and the use of facilities at the Stratton VA Medical Center, Albany, NY, USA. Authors: 1. Kim S. Stote PhD, MPH, RDN, CDN, Stratton VA Medical Center, Albany, NY, 2. Margaret M. Wilson MS, RD, LD/N, CD/N, CNSC, CDCES, Stratton VA Medical Center, Albany, NY, 3. Jean Cottrell PharmD, Stratton VA Medical Center, Albany NY, 4.Tabitha Norris MS, RD, Stratton VA Medical Center, Albany, NY, 5. Joanne Rourke NP, CDCES, Stratton VA Medical Center, Albany NY, 6. Mary Patricia Roy MD, Stratton VA Medical Center, Albany, NY, 7. Aidar R. Gosmanov MD, PhD, US; Stratton VA Medical Center, Albany NY.
Background/Purpose: Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) use has grown rapidly. In clinical trials, CGM and diabetes self-management education and support (DSMES) show clinical benefits such as reduction of HbA1c, reduction of hypoglycemia and the increase of the amount of time glucose values are in target range. However, less is known about the efficacy of CGM use in real world clinical settings. Research Hypothesis and/or Research Questions and Specific
Aims: CGM along with DSMES improves HbA1c and glucose management metrics for clinical care in persons with type 2 diabetes. Methods/Methodology: This retrospective observational study examined twelve months of data collected from existing medical records at the Stratton VA Medical Center, Albany, NY. HbA1c and CGM metrics were analyzed in patients with type 2 diabetes who started to use CGM beginning in January 2019 or later. This study was approved by the IRB of the Stratton VA Medical Center.
Results: Forty men with type 2 diabetes initiated CGM with DSMES. Mean ± SE HbA1c was significantly lowered at 6 months (8.0 ± 0.3% at baseline compared with 7.6 ± 0.2% at 6 months; P = 0.0025) and at 12 months (8.0 ± 0.3% at baseline compared with 7.4 ± 0.2% at 12 months; P = 0.0001). Mean ± SE: time in target range (70-180 mg/dl) was 64.9 ± 3.7% and 64.8 ± 3.7%, time above range (> 180 mg/dl) was 29.8 ± 3.9% and 28.6 ± 3.7%, and time below range ( < 70 mg/dl) was 4.3 ± 0.8% and 3.5 ± 0.8%, at 6 months and 12 months, respectively. Conclusions (Impact on Diabetes Care and Education): These findings suggest that in men with type 2 diabetes, initiation of CGM under supervision of a DSMES specialist may improve glycemic management within 6 months following CGM prescription with further improvements up until 12 months of diabetes technology utilization. Source of Funding for this Research: The study is the result of work supported with resources and the use of facilities at the Stratton VA Medical Center, Albany, NY, USA. Authors: 1. Kim S. Stote PhD, MPH, RDN, CDN, Stratton VA Medical Center, Albany, NY, 2. Margaret M. Wilson MS, RD, LD/N, CD/N, CNSC, CDCES, Stratton VA Medical Center, Albany, NY, 3. Jean Cottrell PharmD, Stratton VA Medical Center, Albany NY, 4.Tabitha Norris MS, RD, Stratton VA Medical Center, Albany, NY, 5. Joanne Rourke NP, CDCES, Stratton VA Medical Center, Albany NY, 6. Mary Patricia Roy MD, Stratton VA Medical Center, Albany, NY, 7. Aidar R. Gosmanov MD, PhD, US; Stratton VA Medical Center, Albany NY.
